 Search
Search


Guidehouse's quarterly newsletter aims to provide global regulatory updates, industry trends, best practices, and detect threats with potential to impact our clients and sector.
As we mark the halfway point in the DORA implementation period, it is crucial to understand DORA’s preparation, scope, and ensure compliance.
DORA Timeline
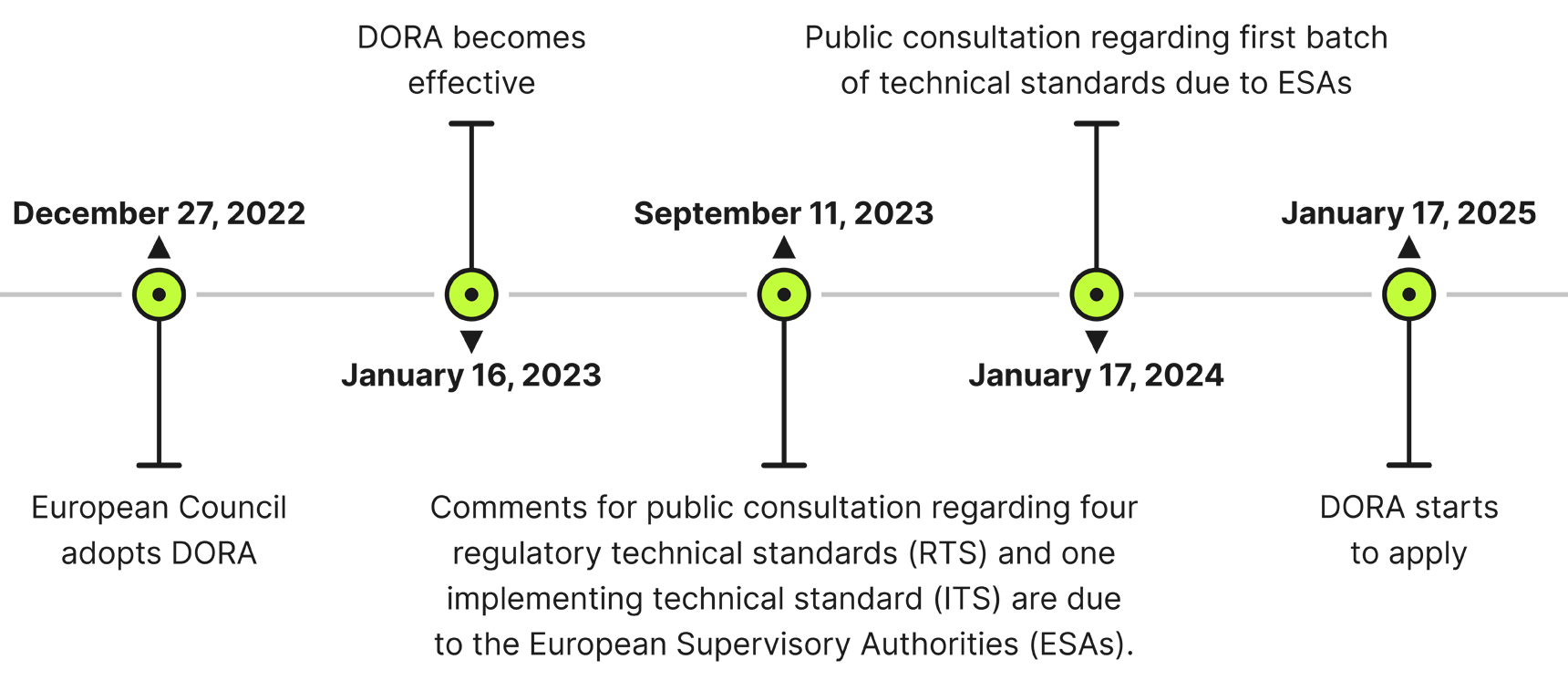
The European Supervisory Authorities (ESAs) launched a public consultation about four technical standards proposed for DORA.
DORA Alignment to Existing Regulations
In the evolving landscape of financial regulations, DORA marks a pivotal step toward a harmonized European regulatory framework, reinforcing principles already embraced by existing regulatory bodies. Notably, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) has been at the forefront, aligning with DORA’s core principles for operational resilience. The FCA, with its stringent approach and emphasis on mapping, testing, and identifying vulnerabilities, mirrors DORA’s commitment to ensuring robust operational structures. As existing regulatory entities pave the way, DORA is poised to further streamline and enhance operational resiliency, ensuring a cohesive and standardized approach across the European financial sector.2 This alignment not only fortifies individual entities but also contributes to the overall strength and stability of the financial ecosystem. Financial services providers outside of Europe should consider how DORA could fuel other regulators to better manage digital risks and operational disruptions. Below are outlined examples of a few of DORA’s key principles:
FCA and DORA Alignment
Operational Resilience Focus — Both the FCA and DORA place emphasis on heightened requirements concerning operational resilience within the financial services sector. In Policy Statement 21/3, the FCA details their collaborative efforts with Bank of England in its capacity of supervising financial market infrastructures (FMIs)—and the Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) to improve the operational resilience of the UK financial sector.3
Critical Third Parties — The FCA, PRA, and the Bank of England propose that certain UK entities supporting the financial services sector designated as “critical third parties” should meet specific operational resilience requirements, aligning with DORA's focus on oversight of Critical Third-Party Providers.
Implementation Period — The FCA provides a 12-month implementation period for regulated organizations to identify important business services, set impact tolerances, carry out mapping and testing, and identify vulnerabilities, similar to the phased implementation approach outlined by DORA.
Hard Deadline — Both the FCA and DORA have strict compliance deadlines. The FCA mandates a deadline of March 2025, requiring firms to conduct mapping and testing to remain within impact tolerances for each important business service.
Consequences of Non-Compliance — Failure to comply with FCA regulations can result in serious consequences, including fines and actions against responsible individuals, aligning with DORA's enforcement measures.
Focus on Cybersecurity — In an interconnected world, both frameworks recognize the increasing importance of operational resilience and cybersecurity, addressing the rise in cyber threats and attacks. Under Principle 11 of the FCA Handbook, firms must report material cyber incidents.4
DORA Emphasizes Technical Adherence
One of DORA’s key focus areas is technical regulations regarding cyber threats. DORA obligations will be detailed by RTS and ITS, which aim to specify and coordinate DORA’s implementation. RTS and ITS frameworks establish measures related to network security, asset management security, data encryption, load testing, physical security, training, and regular logging and reporting. All Information and Communications Technology must be in the risk management framework in case of ICT incidents.
Recognizing the increasing complexity of ICT risks, DORA encourages financial entities to exchange cyber threat information and intelligence among themselves. This includes indicators of compromise, tactics, techniques, procedures, cybersecurity alerts, and configuration tools. The objective is to enhance digital operational resilience by raising awareness of cyber threats, limiting their ability to spread, and supporting defensive capabilities. Importantly, such information exchange is designed to occur within trusted communities of financial entities, ensuring sensitive data protection and governed by rules respecting business confidentiality, personal data protection, and competition policy guidelines.
Best Practices for Reaching Compliance
Regulated entities need to demonstrate robust controls around ICT activities. Therefore, these firms should define a strategy and associated policy, conduct due diligence and risk assessments, and create a map between critical providers and business functions. For example, DORA aligns with certain existing regulations, such as those set forth by the FCA and the Central Bank of Ireland, encompassing aspects such as identifying critical third parties, disaster recovery, business continuity management, and cyber-security guidance. Firms who already comply with these and similar regulations, and have a critical business or essential service orientation, can use their existing compliance practices and build upon them to become DORA-compliant. Additionally, affected firms can establish and maintain resilience ICT systems, develop procedures to log ICT incidents for reporting purposes, and periodically test their ICT systems for risk preparedness.
North America
Retail Payment Activities Act
The Bank of Canada’s Retail Payment Activities Act (RPAA) — which manages operational risks, safeguards end-user funds, and reports incidents for payment service providers (PSPs) — were finalized on November 22, 2023. The goal of the RPAA is to build increased reliability and trust in Canada’s retail payment sector and to increase membership to payments-focused organizations within the Bank of Canada, such as Payments Canada and Canada’s Real-Time Rail. The regulation will go into effect in November 2024 and all regulations must be complied with by September 2025.5
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Cybersecurity Disclosure Rule
The SEC implemented a new disclosure regime that requires covered entities to disclose material cyber incidents, risks, and other cybersecurity governance measures. As of July 2023, publicly traded companies need to report impacts of material cybersecurity incidents within four days of deeming the incident material and must be described in a Form 8K. This standardized approach allows for greater transparency between shareholders and potential investors and publicly traded companies.6 Publicly traded companies need to create mechanisms for reporting and collecting information about material data breaches.
Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) Requires Operational Resilience Framework
The CFTC unanimously approved a proposed rule in December 2023 that would require futures commission merchants, swap dealers, and major swap participants to establish, document, implement, and maintain an Operational Resilience Framework reasonably designed to identify, monitor, manage, and assess risks relating to information and technology security, third-party relationships, and emergencies or other significant disruptions to normal business operations.7 The implementation of the framework signals the efforts by the CFTC to follow the footsteps of the other regulatory agencies and to increase oversight of operational governance.
Europe, Middle East, and Africa
New Critical Third Parties (CTPs) Regulation in United Kingdom
In December, the Bank of England, the FCA, and the PRA proposed a set of regulatory requirements for CTPs for financial services entities. Because CTPs offer critical services to financial services, regulators seek to limit the risks associated with third parties. The Treasury measures CTPs on the materiality of their services to financial services firms; concentration of the services they provide to financial services firms; and other drivers of potential systemic impact. The regulators propose a framework revolving around fundamental rules, operational risk, and resilience requirements. CTPs should familiarize themselves with the new regulatory requirements and assess how their current operations align with the regulatory framework.8
Publication of Critical Third Parties (CTPs) Regulatory Framework Proposal
In December 2023, a proposal to implement regulatory requirements and expectations for CTPs that provide services to authorized persons, relevant service providers, and financial market infrastructure entities (FMIs).9 The key objective of the proposals is to manage potential risks to the stability of, or confidence in, the UK financial system that may arise due to a failure in, or disruption to, the services that a CTP provides to such entities. The Regulatory Framework proposal includes a dual framework for CTPs comprising Fundamental Rules and Operational Risk and Resilience Requirements. The proposals also include some additional obligations outside of the dual framework. According to regulators, the proposal benefits will outweigh the costs, including the enhanced trust and reduced systemic risk.
AT&T Service Outage
More than 70,000 AT&T cellular and internet outages were reported on the morning of February 22, 2024. Although 75% of service was restored by the afternoon of the outage, some AT&T customers could not make emergency calls (such as to 9-1-1).10 Besides individual consumers, small businesses were most heavily impacted by the outage, which temporarily disrupted business operations. There has been no indication that a cyber attack or malicious activity caused the outage. AT&T attributed the outage to a coding error.11 The Federal Communications Commission confirmed their launch of an investigation into the outage.12 The incident represents a growing expectation for transparency and responsiveness from service providers.
Data Breach at Mr. Cooper Group
Data breach at Mr. Cooper Group—one of the U.S.’s largest mortgage providers—affected about 14.7 million people.13 According to the SEC, “substantially all” of the firm’s current and former customers had their information compromised. To avoid further disruptions and enhance resilience, they will be updating their systems to prevent future breaches.
Comcast Account Compromised Through Third Party
Between October 16 and 19, 2023, Comcast reported that information from nearly 36 million accounts had been compromised due to its third-party cloud-computing software. Citrix, who issued the cloud-based software, disclosed a vulnerability in its software on October 10. Citrix is encouraging its customers to purchase software patches to protect against data breaches. Although Comcast has not reported misuse of customers’ compromised information, Google’s Mandiant cybersecurity group reports that “hackers have been exploiting the Citrix bug since at least August” to break into systems.14
China’s Debt Crisis
China faces potential financial crisis as hidden debt within cities and provinces reaches an estimated $7 trillion to $11 trillion, with significant portion at high risk of default.15 Economic slowdown and deflationary pressures pose challenges for local governments to meet interest and principal payments. The government is addressing the issue by swapping hidden debt for explicit government debt, but concerns persist about widespread defaults impacting financial stability. Moody’s has downgraded China’s credit rating to A1 due to potential support for stressed government. Banks hold a substantial portion of the debt, raising fears of a nationwide financial crisis. Efforts to issue special refinancing bonds aim to alleviate immediate liquidity problems, but analysts warn of the need for more substantial debt swaps to address the underlying issues and ensure sustainable growth.
Payment Services Outages
Recent disruptions in payment services affecting Cash App, Square, and Apple Pay caused inconveniences for consumers, delaying service. Notably, Cash App and Square, both under Block, experienced outages on September 7, 2023, resulting in slight delays for peer-to-peer payments, cash-card purchases, and other transactions.16 Apple also faced temporary outages on the morning of December 20, impacting Apple Pay, Card, Cash, and Wallet services.17 The issue specifically affected web and in-app payment features. Although the problem has been resolved, there was a delay in updating the system status page. Given the direct and material impact to individuals, small- and medium-size business (SMBs), and enterprise users of these payment services and wallets, we recommend that those who are dependent on a timely exchange of funds adopt redundancies in methods to send and receive payments, so as not to be left optionless in the instance of an outage, whether planned or unplanned.
Third-Party Risk Management
Companies continue to endure the negative consequences due to lack of oversight of third-party risk management. Drata, a security and compliance automation platform that monitors and collects evidence of a company’s security controls, found that 69% of enterprise companies spend $1,000 or more annually managing risk. However, two in five lack proper staff and resources to thoroughly screen third parties and vendors in a timely manner. In addition, 80% of businesses believe they do not have full visibility into third-parties’ security posture.18 It is evident that third-party risk management continues to pose a large risk to businesses and identifying a tactical strategy for long-term visibility is essential.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Strengthens Cybersecurity and Operational Resilience
AWS has launched two programs aimed at strengthening enterprise cybersecurity and operational resiliency with a focus on SMBs.19 AWS says its Cyber Insurance Competency and Resilience Competency Programs will accelerate the acquisition of cyber insurance and improve the resiliency of workloads using the AWS Cloud and its partners. The cyber insurance expertise will include supporting small and medium-size businesses in cybersecurity as we see an increase in cyber attacks. The Resilience skills of the program will help drive business continuity. In this context, resilience competency programs support companies to increase the resilience of their operations.
AI’s Implementation into Banking Sector
Since its inception in 2022, generative AI has become the focus of financial services institutions due to its ability to quickly synthesize information, analyze large amounts of transactional data, and create personalized customer interactions. While adopting generative AI solutions can save time and reduce personnel costs, they are also costly and require users to consider data quality and hire personnel to help implement AI in existing business frameworks.20
According to International Data Corporation, global spending on AI is anticipated to reach $166 billion in 2023 (with banking making up 13%) and is expected to rise to $450 billion by 2027. Financial services can utilize AI to boost efficiency and reduce long-term costs in functions such as credit issuance, identifying fraudulent behavior, and detecting data breaches.21
Guidehouse is a global AI-led professional services firm delivering advisory, technology, and managed services to the commercial and government sectors. With an integrated business technology approach, Guidehouse drives efficiency and resilience in the healthcare, financial services, energy, infrastructure, and national security markets.